What is ZUS? Polish Social Insurance Explained
ZUS (Zakład Ubezpieczeń Społecznych) is Poland's Social Insurance Institution. If you work in Poland, you'll be paying into ZUS - here's everything you need to know about how it works and what you get in return. This comprehensive guide covers contribution rates, benefits, healthcare access, and answers the most common questions about Poland's social security system.
Table of Contents
ZUS: The Basics
ZUS (Zakład Ubezpieczeń Społecznych) is Poland's social insurance system. Every employee in Poland pays into ZUS, which provides healthcare, pensions, disability benefits, and sick leave coverage. The system operates similarly to social security in other European countries.
Monthly ZUS contributions total approximately 22% of gross salary. While this may appear substantial, these payments secure immediate healthcare access and build future pension entitlements. Unlike general taxation, ZUS maintains individual contribution records that directly determine pension amounts.
ZUS coverage is mandatory for all legal workers in Poland, regardless of nationality. The system includes employees on standard contracts (umowa o pracę), specific task contracts (umowa zlecenie), and certain business-to-business arrangements. EU citizens, non-EU workers with permits, and Polish nationals receive identical treatment under the system.
ZUS provides several immediate benefits beyond future pension rights. Healthcare coverage begins from the first day of employment. Sick leave compensation starts after the employer's initial coverage period ends. Maternity and paternity benefits are calculated based on contribution history. Disability protection activates if work-related or health issues prevent employment.
The contribution calculation uses gross salary as the base, with separate rates for different insurance types. Employers handle all administrative aspects, including payment deadlines and reporting requirements. Workers receive detailed contribution statements and can access their records through the online PUE ZUS portal.
Important: ZUS is not just a tax - it's insurance. You're building up credits for your future pension and getting immediate access to healthcare and other benefits. The more you pay in, the higher your eventual pension will be.
What You Pay Into ZUS
ZUS contribution rates are established by Polish law and apply to gross salary up to annual maximum limits. Most employees remain below these thresholds. Rate adjustments occur periodically through legislative changes, though recent years have seen minimal modifications.
Employers manage contribution calculations, deductions, and transfers to ZUS. Employee portions are deducted from gross salary before net pay calculation. Employer portions represent additional costs beyond employee compensation. All contributions must reach ZUS by the 15th of the following month.
Students under 26 enrolled in full-time education receive exemption from sickness insurance contributions (chorobowe), reducing their total rate by 2.45%. This exemption terminates on the 26th birthday regardless of academic year completion. All other contribution types remain mandatory for student workers.
Employee Contributions
Pension Insurance (emerytalne)
Goes toward your future pension. The more you pay, the higher your pension will be.
Disability Insurance (rentowe)
Covers you if you become unable to work due to disability.
Sickness Insurance (chorobowe)
Pays for sick leave. Students under 26 are exempt from this one.
Health Insurance (zdrowotne)
Gives you access to Polish public healthcare system.
What Your Employer Pays
Your employer also pays additional ZUS contributions on top of your salary:
Important: This employer contribution doesn't come out of your salary - it's an additional cost your employer pays on top of your gross salary.
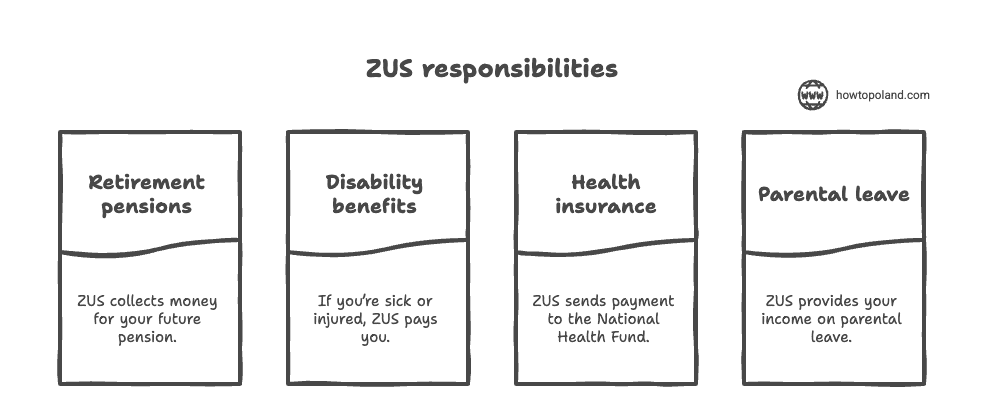
What You Get From ZUS
Healthcare Access
Free access to Polish public healthcare system - doctor visits, hospital stays, emergency care, and prescription medications (with co-pays).
Sick Leave Pay
If you're sick and can't work, ZUS pays 80% of your average salary after the first 33 days (your employer covers the first 33 days at 80%).
Future Pension
Your contributions build up credits for retirement. The pension amount depends on how much you've paid in and how long you've worked.
Disability Benefits
If you become unable to work due to illness or injury, ZUS provides disability pension based on your contribution history.
Maternity/Paternity
Maternity leave (20 weeks), paternity leave (2 weeks), and parental leave benefits are all paid through ZUS based on your average earnings.
Survivor Benefits
If something happens to you, your family can receive survivor benefits from ZUS based on your contribution record.
Healthcare Access & Coverage
ZUS health insurance provides comprehensive medical coverage for all insured workers in Poland. The system grants immediate access to public healthcare services, including primary care, specialist consultations, hospital treatments, and emergency medical services.
Coverage activates from the first day of employment without waiting periods. Insured individuals receive health insurance cards valid at all public healthcare facilities throughout Poland. The system operates under the National Health Fund (NFZ), which manages healthcare delivery while ZUS collects contributions.
Primary care requires registration with a family physician who serves as the first point of contact for medical services and provides referrals to specialists. Emergency services operate independently without referral requirements, ensuring immediate access to urgent medical care.

Photo by pexels.com
What's Covered
- Doctor visits and consultations
- Hospital stays and treatments
- Emergency medical care
- Prescription medications (with co-pays)
- Specialist referrals
How to Access Healthcare
Additional Coverage:
Many employers provide supplementary private health insurance to reduce waiting times for specialist consultations and enable access to private medical facilities.
Polish Pension System Explained
Poland operates a defined contribution pension system where benefits correlate directly with individual contribution amounts and duration. Monthly pension contributions accumulate in personal accounts maintained by ZUS. Account holders can monitor balances through the PUE ZUS online platform.
Standard retirement age is 67 years for both genders. Early retirement becomes available after 25 years of contributions (women) or 30 years (men), though benefits are permanently reduced. Most workers continue until standard retirement age to maximize pension amounts.
Pension calculations employ complex formulas, but follow basic principles: higher contributions and longer contribution periods generate larger pensions. The system includes minimum pension guarantees where state supplements apply if calculated benefits fall below established thresholds.
International workers benefit from pension portability agreements. EU citizens can typically combine Polish contributions with home country systems. Poland maintains bilateral social security agreements with numerous non-EU countries, including the United States, Canada, and Australia, enabling contribution recognition across borders.
How It Works
- 1Your contributions build up "pension capital" over time
- 2The more you contribute, the higher your pension will be
- 3Retirement age is 67 for both men and women
- 4You can check your pension status online through PUE ZUS
Estimated Pension Amounts
Minimum pension eligibility
Standard full career
Long career with higher contributions
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I have to pay ZUS if I work in Poland?▼
Yes, if you're employed in Poland (UoP contract) or working as a contractor (UZ), ZUS contributions are mandatory. B2B contractors can sometimes opt out of certain parts, but health insurance is always required.
Can I use my ZUS health insurance right away?▼
Yes, once you start paying ZUS contributions, you have immediate access to Polish public healthcare. You'll get a health insurance card that you can use at any public clinic or hospital in Poland.
What happens to my ZUS if I leave Poland?▼
Your ZUS contributions don't disappear. Poland has social security agreements with many countries, so your contributions may count toward benefits in your home country. You might also be able to get a partial refund in some cases.
How much pension will I get from ZUS?▼
Your pension depends on how much you've contributed and for how long. As a rough estimate, if you work 35 years in Poland, your pension might be around 40-60% of your average salary. ZUS has online calculators to give you better estimates.
Can students avoid paying ZUS?▼
Students under 26 are exempt from sickness insurance (chorobowe), but they still pay pension, disability, and health insurance. If you're a full-time student working part-time, you might qualify for reduced rates.
Is ZUS health insurance good enough or do I need private?▼
ZUS health insurance covers all basic medical needs - doctor visits, hospital stays, surgeries, and medications. Many people also get private insurance through their employer for faster access to specialists and private hospitals.
What's the difference between ZUS and NFZ?▼
ZUS collects your health insurance contributions, but NFZ (National Health Fund) actually manages the healthcare system. Think of ZUS as the collector and NFZ as the provider. You deal with ZUS for contributions and NFZ for healthcare services.
Can I check my ZUS contributions online?▼
Yes, ZUS has an online portal (PUE ZUS) where you can check your contribution history, download documents, and estimate your future pension. You'll need to register with your PESEL number and create an account.
Calculate Your ZUS Contributions
Want to see exactly how much you'll pay to ZUS from your salary? Our Polish salary calculator shows the exact breakdown of all your contributions and what you'll take home.
Calculate Your Net Salary